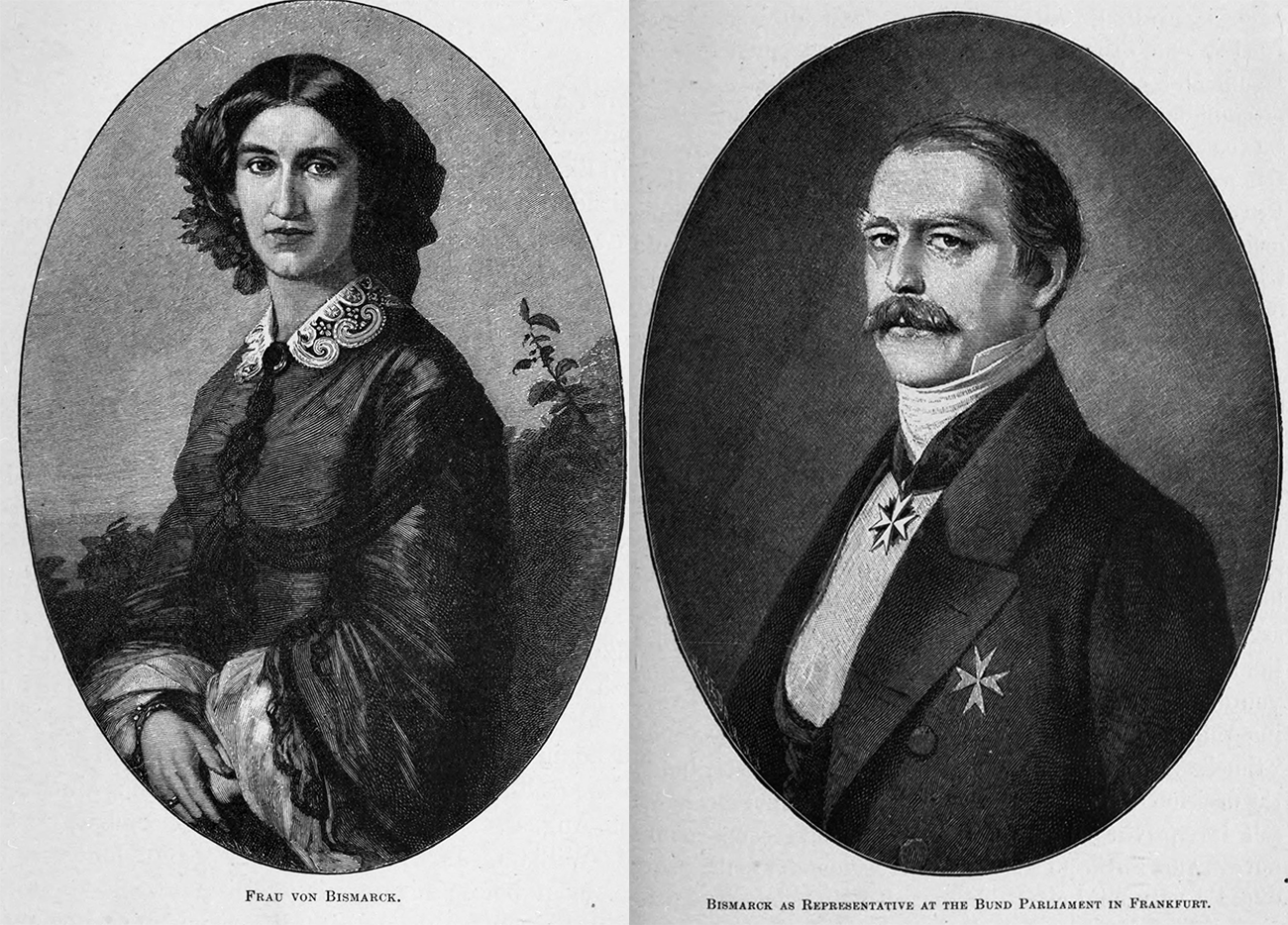READING HALL
DOORS OF WISDOM

 |
READING HALLDOORS OF WISDOM |
 |
 |
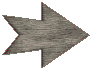 |
BISMARCKAND THE FOUNDATION OF THE GERMAN EMPIRECHAPTER II.
EARLY LIFE. 1821-1847.
Of the boy's early life we know little. His mother was ambitious for her sons;
Otto from his early years she designed for the Diplomatic Service; she seems to
have been one of those women who was willing to sacrifice the present happiness
of her children for their future advancement. When only six years old the boy
was sent away from home to a school in Berlin. He was not happy there; he pined
for the free life of the country, the fields and woods and animals; when he saw
a plough he would burst into tears, for it reminded him of his home. The
discipline of the school was hard, not with the healthy and natural hardships
of life in the open air, but with an artificial Spartanism,
for it was the time when the Germans, who had suddenly awoke to feelings of patriotism and a love of war to which they had long been
strangers, under the influence of a few writers, were throwing all their
energies into the cultivation of physical endurance. It was probably at this
time that there was laid the foundation of that dislike for the city of Berlin
which Bismarck never quite overcame; and from his earliest years he was
prejudiced against the exaggerated and affected Teutonism which was the fashion after the great war. A few years later his parents came
to live altogether in the town; then the boy passed on to the Gymnasium,
boarding in the house of one of the masters. The teaching in this school was
supplemented by private tutors, and he learned at this time the facility in the
use of the English and French languages which in after years was to be of great
service to him. The education at school was of course chiefly in the classical
languages; he acquired a sufficient mastery of Latin. There is no evidence that
in later life he continued the study of classical literature. In his
seventeenth year he passed the Abiturienten examination, which admitted him as a student to the university and entitled him
to the privilege of serving in the army for one instead of three years. His
leaving certificate tells us that his conduct and demeanour towards his comrades and teachers were admirable, his abilities considerable,
and his diligence fair.
The next year he
passed in the ordinary course to the university, entering at Göttingen; the
choice was probably made because of the celebrity which that university had
acquired in law and history. It is said that he desired to enter at Heidelberg,
but his mother refused her permission, because she feared that he would learn
those habits of beer-drinking in which the students of that ancient seat of
learning have gained so great a proficiency; it was, however, an art which, as
he found, was to be acquired with equal ease at Göttingen. The young Bismarck
was at this time over six feet high, slim and well
built, of great physical strength and agility, a good fencer, a bold rider, an
admirable swimmer and runner, a very agreeable companion; frank, cheerful, and
open-hearted, without fear either of his comrades or of his teachers. He
devoted his time at Göttingen less to learning than to social life; in his
second term he entered the Corps of the Hanoverians and was quickly noted for
his power of drinking and fighting; he is reported to have fought twenty-six
duels and was only wounded once, and that wound was caused by the breaking of
his opponent's foil. He was full of wild escapades, for which he was often
subjected to the ordinary punishments of the university.
To many Germans,
their years at the university have been the turning-point of their life; but it
was not so with Bismarck. To those who have been brought up in the narrow
surroundings of civic life, student days form the single breath of freedom
between the discipline of a school and the drudgery of an office. To a man who,
like Bismarck, was accustomed to the truer freedom of the country, it was only
a passing phase; as we shall see, it was not easy to tie him down to the
drudgery of an office. He did not even form many friendships which he continued
in later years; his associates in his corps must have been chiefly young
Hanoverians; few of his comrades in Prussia were to be found at Göttingen; his
knowledge of English enabled him to make the acquaintance of the Americans and
English with whom Göttingen has always been a favourite university; among his fellow-students almost the only one with whom in after
life he continued the intimacy of younger days was Motley. We hear little of
his work; none of the professors seem to have left any marked influence on his
mind or character; indeed they had little opportunity
for doing so, for after the first term his attendance at lectures almost
entirely ceased. Though never a student, he must have been at
all times a considerable reader; he had a retentive memory and quick
understanding; he read what interested him; absorbed, understood, and retained
it. He left the university with his mind disciplined indeed but not drilled; he
had a considerable knowledge of languages, law, literature, and history; he had
not subjected his mind to the dominion of the dominant Hegelian philosophy, and
to this we must attribute that freshness and energy which distinguishes him
from so many of his ablest contemporaries; his brain was strong, and it worked
as easily and as naturally as his body; his knowledge was more that of a man of
the world than of a student, but in later life he was always able to understand
the methods and to acquire the knowledge of the subjects he required in his
official career. History was his favourite study; he
never attempted, like some statesmen, to write; but if his knowledge of history
was not as profound as that of a professed historian, he was afterwards to show
as a parliamentary debater that he had a truer perception of the importance of
events than many great scholars who have devoted their lives to historical
research, and he was never at a loss for an illustration to explain and justify
the policy he had assumed. For natural science he shewed little interest, and
indeed at that time it scarcely could be reckoned among the ordinary subjects
of education; philosophy he pursued rather as a man than as a student, and we
are not surprised to find that it was Spinoza rather than Kant or Fichte or
Hegel to whom he devoted most attention, for he cared more for principles of
belief and the conduct of life than the analysis of the intellect.
His university
career does not seem to have left any mark on his political principles; during
just those years, the agitation of which the universities had long been the
scene had been forcibly repressed; it was the time of deep depression which
followed the revolution of 1830, and the members of the aristocratic corps to
which he belonged looked with something approaching contempt on this Burschenschaft, as the union was called, which propagated
among the students the national enthusiasm.
After spending
little more than a year at Göttingen, he left in September, 1833; in May of the
following year he entered as a student at Berlin, where he completed his
university course; we have no record as to the manner in which he spent the
winter and early spring, but we find that when he applied to Göttingen for
permission to enter at Berlin, it was accorded on condition that he sat out a
term of imprisonment which he still owed to the university authorities. During
part of his time in Berlin he shared a room with Motley. In order to prepare
for the final examination he engaged the services of a
crammer, and with his assistance, in 1835, took the degree of Doctor of Law and
at once passed on to the public service.
He had, as we have
seen, been destined for the Diplomatic Service from early life; he was well
connected; his cousin Count Bismarck-Bohlen stood in high favour at Court. He
was related to or acquainted with all the families who held the chief posts
both in the military and civil service; with his great talents and social gifts
he might therefore look forward to a brilliant career. Any hopes, however, that
his mother might have had were destined to be disappointed; his early official
life was varied but short. He began in the judicial department and was
appointed to the office of Auscultator at Berlin, for in the German system the
judicature is one department of the Civil Service. After a year he was at his
own request transferred to the administrative side and to Aix-la-Chapelle; it is
said that he had been extremely pained and shocked by the manner
in which the officials transacted the duties of their office and
especially by their management of the divorce matters which came before the
court. The choice of Aix-la-Chapelle was probably owing to
the fact that the president of that province was Count Arnim of Boytzenburg, the head of one of the most numerous and
distinguished families of the Mark, with so many members of which Bismarck was
in later years to be connected both for good and evil. Count Arnim was a man of
considerable ability and moderate liberal opinions, who a few years later rose
to be the first Minister-President in Prussia. Under him Bismarck was sure to
receive every assistance. He had to pass a fresh examination, which he did with
great success. His certificate states that he shewed thoroughly good school studies, and was well grounded in law; he had thought over
what he had learnt and already had acquired independent opinions. He had
admirable judgment, quickness in understanding, and a readiness in giving
verbal answers to the questions laid before him; we see all the qualities by
which he was to be distinguished in after life. He entered on his duties at
Aix-la-Chapelle at the beginning of June; at his own request Count Arnim wrote
to the heads of the department that as young Bismarck was destined for a
diplomatic career they were to afford him every
opportunity of becoming acquainted with all the different sides of the
administrative work and give him more work than they otherwise would have done;
he was to be constantly occupied. His good resolutions did not, however,
continue long; he found himself in a fashionable watering-place, his knowledge
of languages enabled him to associate with the French and English visitors, he
made excursions to Belgium and the Rhine, and hunting expeditions to the
Ardennes, and gave up to society the time he ought to have spent in the office.
The life at Aix was not strict and perhaps his amusements were not always
edifying, but he acquired that complete ease in cosmopolitan society which he
could not learn at Göttingen or Berlin, and his experiences during this year
were not without use to him when he was afterwards placed in the somewhat
similar society of Frankfort. This period in his career did not last long; in June, 1837, we find him applying for leave of absence on
account of ill-health. He received leave for eight days, but he seems to have
exceeded this, for four months afterwards he writes from Berne asking that his
leave may be prolonged; he had apparently gone off for a long tour in
Switzerland and the Rhine. His request was refused; he received a severe
reprimand, and Count Arnim approved his resolution to return to one of the
older Prussian provinces, "where he might shew an activity in the duties
of his office which he had in vain attempted to attain in the social conditions
of Aachen."
He was transferred
to Potsdam, but he remained here only a few weeks; he had not as yet served in
the army, and he now began the year as a private soldier which was required
from him; he entered the Jaeger or Rifles in the Garde Corps which was stationed at Potsdam, but after a few weeks was transferred to the
Jaeger at Stettin. The cause seems to have been partly the ill-health of his
mother; she was dying, and he wished to be near her; in those days the journey
from Berlin to Pomerania took more than a day; besides this there were
pecuniary reasons. His father's administration of the family estates had not
been successful; it is said that his mother had constantly pressed her husband
to introduce innovations, but had not consistently
carried them out; this was a not unnatural characteristic in the clever and
ambitious woman who wished to introduce into agricultural affairs those habits
which she had learnt from the bureaucrats in Berlin. However this may be,
matters had now reached a crisis; it became necessary to sell the larger part
of the land attached to the house at Schoenhausen,
and in the next year, after the death of Frau von Bismarck, which took place on
January 1, 1839, it was decided that Herr von Bismarck should in future live at Schoenhausen with his only daughter, now a girl of
twelve years of age, while the two brothers should undertake the management of
the Pomeranian estates.
So it came about that
at the age of twenty-four all prospect of an official career had for the time
to be abandoned, and Otto settled down with his brother to the life of a
country squire. It is curious to notice that the greatest of his
contemporaries, Cavour, went through a similar training. There was, however, a
great difference between the two men: Cavour was in this as in all else a
pioneer; when he retired to his estate he was opening out new forms of activity
and enterprise for his countrymen; Bismarck after the few wild years away from
home was to go back to the life which all his ancestors had lived for five
hundred years, to become steeped in the traditions of his country and his
caste. Cavour always points the way to what is new, Bismarck again brings into honour what men had hastily thought was antiquated. He had
to some extent prepared himself for the work by attending lectures at a newly
founded agricultural college in the outskirts of Greifswald. The management of
the estate seems to have been successful; the two brothers started on their
work with no capital and no experience, but after three or four years by
constant attention and hard work they had put the affairs in a satisfactory
state. In 1841, a division was made; Otto had wished this to be done before, as
he found that he spent a good deal more money than his brother and was gaining
an unfair advantage in the common household; from this time he took over Kniephof, and there he lived for the next four years, while
his brother took up his abode four miles off at Kulz,
where he lived till his death in 1895. Otto had not indeed given up the habits
he had learnt at Göttingen; his wild freaks, his noisy entertainments, were the
talk of the countryside; the beverage which he has made classical, a mixture of
beer and champagne, was the common drink, and he was known far and wide as the
mad Bismarck. These acts of wildness were, however, only a small part of his
life; he entered as a lieutenant of Landwehr in the cavalry and thereby became
acquainted with another form of military service. It was while he was at the
annual training that he had an opportunity of shewing his physical strength and
courage. A groom, who was watering horses in the river, was swept away by the
current; Bismarck, who was standing on a bridge watching them, at once leaped
into the river, in full uniform as he was, and with great danger to himself
saved the drowning man. For this he received a medal for saving life. He
astonished his friends by the amount and variety of his reading; it was at this
time that he studied Spinoza. It is said that he had among his friends the
reputation of being a liberal; it is probable enough that he said and did many
things which they did not understand; and anything they did not understand
would be attributed to liberalism by the country gentlemen of Pomerania; partly
no doubt it was due to the fact that in 1843 he came
back from Paris wearing a beard. We can see, however, that he was restless and
discontented; he felt in himself the possession of powers which were not being
used; there was in his nature also a morbid restlessness, a dissatisfaction
with himself which he tried to still but only increased by his wild excesses.
As his affairs became more settled he travelled; one
year he went to London, another to Paris; of his visit to England we have an
interesting account in a letter to his father. He landed in Hull, thence he
went to Scarborough and York, where he was hospitably received by the officers
of the Hussars; "although I did not know any of them, they asked me to
dinner and shewed me everything"; from York he went to Manchester, where
he saw some of the factories.
"Generally speaking I cannot praise too highly the extraordinary
courtesy and kindness of English people, which far surpass what I had expected;
even the poor people are pleasant, very unassuming, and easy to get on with
when one talks to them. Those who come much into intercourse with strangers--cab-drivers, porters, etc.--naturally have a tendency to
extortion, but soon give in when they see that one understands the language and
customs and is determined not to be put upon. Generally I find the life much cheaper than I expected."
In 1844, his
sister, to whom he was passionately devoted, was married to an old friend,
Oscar von Arnim. Never did an elder brother write to his young sister more
delightful letters than those which she received from him; from them we get a
pleasant picture of his life at this time. Directly after the wedding, when he
was staying with his father at Schoenhausen, he
writes:
"Just now I am
living here with my father, reading, smoking, and walking; I help him to eat
lamperns and sometimes play a comedy with him which it pleases him to call
fox-hunting. We start out in heavy rain, or perhaps with 10 degrees of frost,
with Ihle, Ellin, and Karl;
then in perfect silence we surround a clump of firs with the most sportsmanlike
precautions, carefully observing the wind, although we all, and probably father
as well, are absolutely convinced that there is not a living creature in it except
one or two old women gathering firewood. Then Ihle,
Karl, and the two dogs make their way through the cover, emitting the most
strange and horrible sounds, especially Ihle; father
stands there motionless and on the alert with his gun cocked, just as though he
really expected to see something. Ihle comes out just
in front of him, shouting 'Hoo lala,
hey heay, hold him, hie, hie,' in the strangest and
most astonishing manner. Then father asks me if I have seen nothing, and I with
the most natural tone of astonishment that I can command, answer 'No, nothing
at all.' Then after abusing the weather we start off
to another wood, while Ihle with a confidence that he
assumes in the most natural manner praises its wealth in game, and there we
play over the game again dal segno. So it goes on for
three or four hours; father's, Ihle's, and Fingal's
passion does not seem to cool for a moment. Besides that, we look at the orange
house twice a day and the sheep once a day, observe the four thermometers in
the room once every hour, set the weather-glass, and,
since the weather has been fine, have set all the clocks by the sun and
adjusted them so closely that the clock in the dining-room is the only one
which ever gives a sound after the others have struck. Charles V. was a stupid
fellow. You will understand that with so multifarious an occupation I have
little time left to call on the clergymen; as they
have no vote for the election it was quite impossible.
"The Elbe is
full of ice, the wind E.S.E., the latest thermometer from Berlin shews 8
degrees, the barometer is rising and at 8.28. I tell you this as an example how
in your letters you might write to father more the small events of your life;
they amuse him immensely; tell him who has been to see you, whom you have been
calling on, what you had for dinner, how the horses are, how the servants
behave, if the doors creak and the windows are firm--in short, facts and
events. Besides this, he does not like to be called papa, he dislikes the
expression. Avis au lecteur."
On another occasion
he says:
"Only with
difficulty can I resist the temptation of filling a whole letter with
agricultural lamentations over frosts, sick cattle, bad reap, bad roads, dead
lambs, hungry sheep, want of straw, fodder, money, potatoes, and manure;
outside Johann is persistently whistling a wretched schottische out of tune,
and I have not the cruelty to interrupt it, for he seeks to still by music his
violent love-sickness."
Then we have long
letters from Nordeney, where he delighted in the sea,
but space will not allow us to quote more. It is only in these letters, and in
those which he wrote in later years to his wife, that we see the natural
kindliness and simplicity of his disposition, his love of nature, and his great
power of description. There have been few better letter-writers in Germany or
any other country.
His ability and
success as an agriculturist made a deep impression on his neighbours.
As years went on he became much occupied in local
business; he was appointed as the representative of his brother, who was Landrath for the district; in 1845 he was elected one of
the members for the Provincial Diet of Pomerania. He also had a seat in the
Diet for the Saxon province in which Schoenhausen was
situated. These local Diets were the only form of representative government
which existed in the rural districts; they had little power, but their opinion
was asked on new projects of law, and they were officially regarded as an
efficient substitute for a common Prussian Parliament. Many of his friends,
including his brother, urged him again to enter the public service, for which
they considered he was especially adapted; he might have had the post of Royal
Commissioner for Improvements in East Prussia.
He did make one attempt
to resume his official career. At the beginning of 1844 he returned to Potsdam
and took up his duties as Referendar, but not for
long; he seems to have quarrelled with his superior.
The story is that he called one day to ask for leave of absence; his chief kept
him waiting an hour in the anteroom, and when he was admitted asked him curtly,
"What do you want?" Bismarck at once answered, "I came to ask
for leave of absence, but now I wish for permission to send in my resignation."
He was clearly deficient in that subservience and ready obedience to authority
which was the best passport to promotion in the Civil Service; there was in his
disposition already a certain truculence and impatience. From this time he nourished a bitter hatred of the Prussian bureaucracy.
This did not,
however, prevent him carrying out his public duties as a landed proprietor. In
1846 we find him taking much interest in proposals for improving the management
of the manorial courts; he wished to see them altered so as to give something
of the advantages of the English system; he regrets the "want of corporate
spirit and public feeling in our corn-growing aristocracy"; "it is
unfortunately difficult among most of the gentlemen to awake any other idea
under the words 'patrimonial power' but the calculation whether the fee will
cover the expenses." We can easily understand that the man who wrote this
would be called a liberal by many of his neighbours;
what he wanted, however, was a reform which would give life, permanency, and
independence to an institution which like everything else was gradually falling
before the inroads of the dominant bureaucracy. The same year he was appointed
to the position of Inspector of Dykes for Jerichow.
The duties of this office were of considerable importance for Schoenhausen and the neighbouring estate; as he writes, "it depends on the managers of this office whether
from time to time we come under water or not." He often refers to the
great damages caused by the floods; he had lost many of his fruit-trees, and
many of the finest elms in the park had been destroyed by the overflowing of
the Elbe.
As Bismarck grew in
age and experience he associated more with the neighbouring families. Pomerania was at this time the centre of a curious religious movement; the leader was Herr
von Thadden, who lived at Triglaff,
not many miles from Kniephof. He was associated with
Herr von Semft and three brothers of the family of
Below. They were all profoundly dissatisfied with the rationalistic religion
preached by the clergy at that time, and aimed at
greater inwardness and depth of religious feeling. Herr von Thadden started religious exercises in his own house, which were attended not only by
the peasants from the village but by many of the country gentry; they desired
the strictest enforcement of Lutheran doctrine, and wished the State directly to support the Church. This tendency of thought
acquired greater importance when, in 1840, Frederick William IV succeeded to
the throne; he was also a man of deep religious feeling, and under his reign
the extreme Lutheran party became influential at Court. Among the ablest of
these were the three brothers von Gerlach. One of them, Otto, was a theologian;
another, Ludwig, was Over-President of the Saxon province, and with him Bismarck
had much official correspondence; the third, Leopold, who had adopted a
military career, was attached to the person of the King and was in later years
to have more influence upon him than anyone except perhaps Bunsen. The real
intellectual leader of the party was Stahl, a theologian.
From about the year
1844 Bismarck seems to have become very intimate with this religious coterie;
his friend Moritz v. Blankenburg had married Thadden's daughter and Bismarck was constantly a visitor at Triglaff. It was at Blankenburg's wedding that he first met Hans v. Kleist, who was in later years to be one of
his most intimate friends. He was, we are told, the most delightful and
cheerful of companions; in his tact and refinement he showed an agreeable
contrast to the ordinary manners of Pomerania. He often rode over to take part
in Shakespeare evenings, and amused them by accounts
of his visit to England. He was present occasionally at the religious meetings
at Triglaff, and though he never quite adopted all
the customs of the set the influence on him of these older men was for the next
ten years to govern all his political action. That he was not altogether at one
with them we can understand, when we are told that at Herr von Thadden's house it would never have occurred to anyone even
to think of smoking. Bismarck was then, as in later life, a constant smoker.
The men who met in
these family parties in distant Pomerania were in a few years to change the
whole of European history. Here Bismarck for the first time saw Albrecht von Roon, a cousin of the Blankenburgs,
then a rising young officer in the artillery; they often went out shooting
together. The Belows, Blankenburgs,
and Kleists were to be the founders and leaders of
the Prussian Conservative party, which was Bismarck's only support in his great
struggle with the Parliament; and here, too, came the men who were afterwards
to be editors and writers of the Kreuz Zeitung.
The religious
convictions which Bismarck learnt from them were to be lasting, and they profoundly
influenced his character. He had probably received little religious training
from his mother, who belonged to the rationalistic school of thought. It was by
them that his monarchical feeling was strengthened. It is not at first apparent
what necessary connection there is between monarchical government and Christian
faith. For Bismarck they were ever inseparably bound together; nothing but
religious belief would have reconciled him to a form of government so repugnant
to natural human reason. "If I were not a Christian, I would be a
Republican," he said many years later; in Christianity he found the only
support against revolution and socialism. He was not the man to be beguiled by
romantic sentiment; he was not a courtier to be blinded by the pomp and
ceremony of royalty; he was too stubborn and independent to acquiesce in the
arbitrary rule of a single man. He could only obey the king if the king himself
held his authority as the representative of a higher power. Bismarck was
accustomed to follow out his thought to its conclusions. To whom did the king
owe his power? There was only one alternative: to the people or to God. If to
the people, then it was a mere question of convenience whether the monarchy were continued in form; there was little to choose between a
constitutional monarchy where the king was appointed by the people and
controlled by Parliament, and an avowed republic. This was the principle held
by nearly all his contemporaries. He deliberately rejected it. He did not hold
that the voice of the people was the voice of God. This belief did not satisfy
his moral sense; it seemed in public life to leave all to interest and ambition
and nothing to duty. It did not satisfy his critical intellect; the word
"people" was to him a vague idea. The service of the People or of the
King by the Grace of God, this was the struggle which was soon to be fought
out.
Bismarck's
connection with his neighbours was cemented by his
marriage. At the beginning of 1847, he was engaged to a Fräulein von Puttkammer, whom he had first met at the Blankenburgs' house; she belonged to a quiet and religious
family, and it is said that her mother was at first filled with dismay when she
heard that Johanna proposed to marry the mad Bismarck. He announced the
engagement to his sister in a letter containing the two words, "All
right," written in English. Before the wedding could take place, a new
impulse in his life was to begin. As representative of the lower nobility he
had to attend the meeting of the Estates General which had been summoned in
Berlin. From this time the story of his life is interwoven with the history of
his country.
CHAPTER III.
THE REVOLUTION.1847-1852.
|
 |
 |